Friday, March 16, 2012
Crossing over into the dark side...
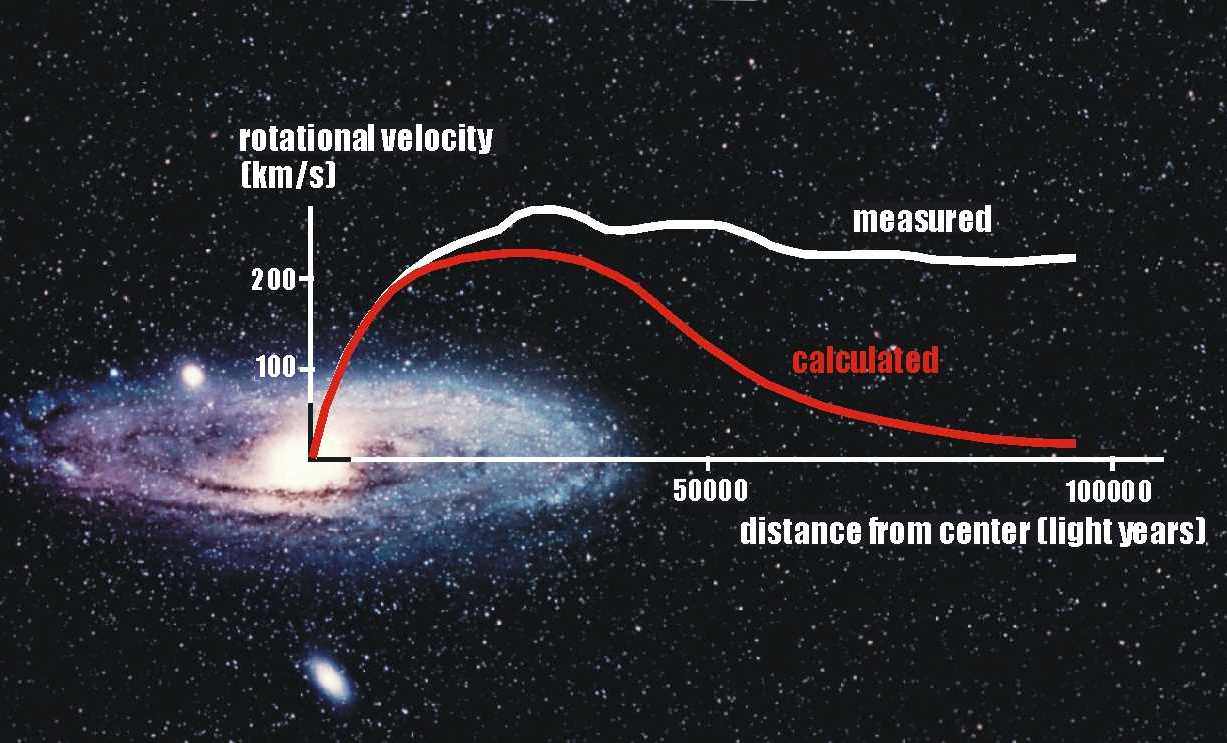
One of the many challenges facing astronomers today is the question of dark matter. What is it? what is it made out of ? and why can't we see it? So far there are only speculations as to what it could possibly be. Before I go into all sorts of details let me talk a bit about what is meant by dark matter. Imagine looking at a galaxy and plotting a graph measuring the rotational velocity of stars around the galactic center, and the distance to their orbits. You will notice that instead of the curve declining as you go further out, as is expected, it remains constant. In layman's terms most of the galaxies' mass is concentrated in its bulge so stars nearest the lump of mass should orbit faster whereas the stars farthest away from the center should orbit slower. There are no visible or detectable objects outside the disk of the galaxy, but according to the galactic rotation curve there must be some unseen matter contributing to the overall mass of the galaxy.
Since it does not emit any light scientists call it "dark" matter. Many scientists believe it might consist of particles called WIMPs(Weakly Interacting Massive Particles) and MACHOs (Massive Compact Halo Objects). An example of a WIMP is a subatomic particle that is not made up of normal matter such as a neutrino, axion, and neutralino. They are said to be weak because they can pass through ordinary matter without any effects. MACHO's on the other hand can range in size from the size of a planet to the size of a black hole, and are made out of ordinary matter. They are objects so faint that they aren't detectable by our instruments. They do, however, at times make themselves known by causing gravitational lensing.
It is interesting that something we can't see can make up 23% of the universe! Perhaps in the future scientists will be able to to say with certainty what this rare and enigmatic substance really is.
It is interesting that something we can't see can make up 23% of the universe! Perhaps in the future scientists will be able to to say with certainty what this rare and enigmatic substance really is.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)