Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Hit the road Pluto...
Ever wondered why Pluto is no longer a planet? I know I have. Ever since I was old enough to go to school I was taught that there were 9 planets in the solar system, but now there are only 8. How can this be? Well, it seems that scientists had a meeting in Prague, in the Czech Republic to discuss what constitutes a "planet." By the end of it they had conjured up a new definition for the term, and Pluto just didn't cut it and was dubbed a dwarf planet. In recent years more Pluto-sized objects have been discovered just outside the orbit: forty-four to be exact and still counting!
The debate was centered on whether to consider these objects planets, and keep on expanding our solar system or simply reconsider the characteristics a body must have to be classified as a planet. The term planet is now defined as a body large enough to become round due to the force of gravity, and having the capability to dominate the neighborhood around its orbit. Pluto's size is small in comparison to other planets, and its moon is about half its size while all "true" planets are larger than their moons. In addition, Pluto doesn't dominate since there are plenty of debris that crosses its path without being swept up by it.
So long Pluto...
Sunday, February 5, 2012
How are stars born?

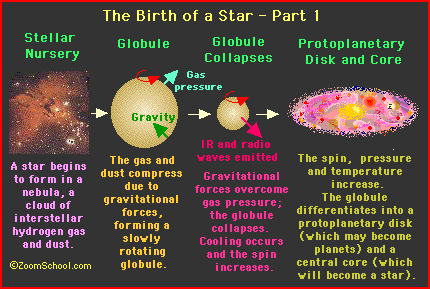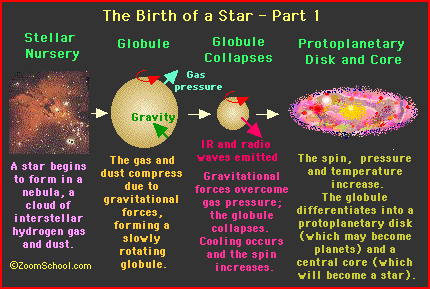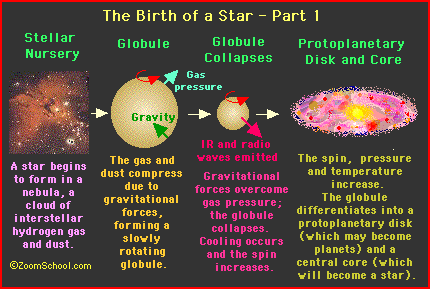
Stars are born from clouds of interstellar dust, and gas called molecular clouds. Gravity draws the debris from hundreds of exploding stars together over the course of millions of years. These clouds, or nebulae, are made up of 98% helium and hydrogen, 1.4% hydrogen compounds, and 6% rocks and metals. In order for stars to form the dust grains must block light from other celestial bodies to allow the formation of molecular hydrogen. Furthermore, the MC (molecular cloud) , must exhibit low temperatures, about 10-30K, and high densities of typically 300 molecules per cubic centimeter, otherwise stars cannot form. In low density nebulae, the grains are spread out allowing the passing through of ultra-violet (UV) photons, responsible for the photo-dissociation, meaning that the energy from the photon breaks the molecule apart , thus
impeding the formation of molecular
hydrogen.
Debris keep collecting together, and soon the
cloud gradually collapses in on itself as more, and more material clumps
together at the center. Molecules, rotating faster at the center, heat up as
atoms get packed together because gravity causes the MC to contract (shrink). At
first,the bulk of the cloud is transparent, and heat escapes, but when it
becomes opaque, or denser, the temperature rises. When internal pressure halts
the collapse of the cloud a protostar* is formed. Eventually the core
becomes hot enough to fuse hydrogen into helium, and at this point a star
is born!
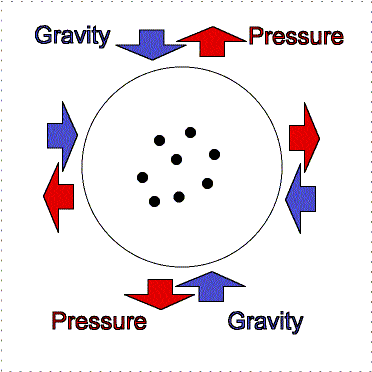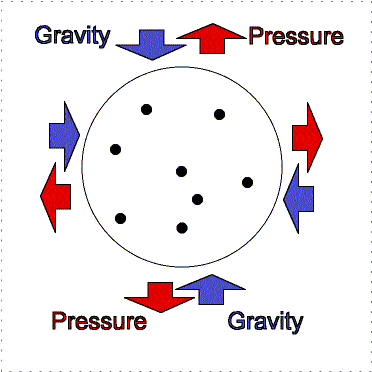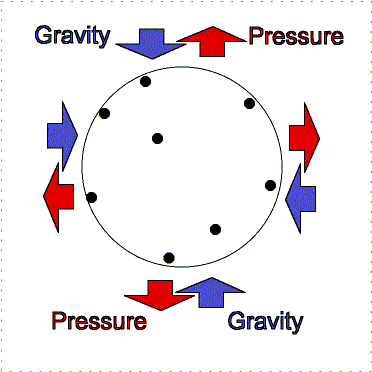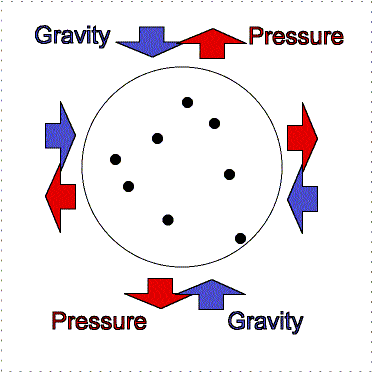 To understand this fully, we must look at the
ongoing battle between gas pressure and gravity. If gravity can overcome the
outward push of gas pressure within the gas cloud, which depends on density and
temperature, than the creation of a star is possible. When gravity makes
a cloud contract, the internal pressure and temperature
increases. It converts some of it's gravitational potential energy into
thermal energy, and quickly rids itself of any thermal energy build up
otherwise thermal pressure would halt the formation of a star, and central
temperature would remain fixed. Constant collisions between gas molecules
transform thermal energy into photons, and as long as the photons are able to
escape then the temperature is kept low.
To understand this fully, we must look at the
ongoing battle between gas pressure and gravity. If gravity can overcome the
outward push of gas pressure within the gas cloud, which depends on density and
temperature, than the creation of a star is possible. When gravity makes
a cloud contract, the internal pressure and temperature
increases. It converts some of it's gravitational potential energy into
thermal energy, and quickly rids itself of any thermal energy build up
otherwise thermal pressure would halt the formation of a star, and central
temperature would remain fixed. Constant collisions between gas molecules
transform thermal energy into photons, and as long as the photons are able to
escape then the temperature is kept low.
Nevertheless, there comes a point where the cloud cannot radiate away thermal energy as it becomes smaller, and denser. The energy then becomes trapped within, and the temperature rises thus slowing down the collapse of the cloud. The dense center becomes a protostar with a core not yet hot enough for nuclear fusion.* It may remain a protostar for 100,000 years or more depending on its mass. The random motion of gas particles, due to the high temperatures, also leads to an overall rotation. This rotation starts out being very slow, but later picks up speed as the cloud becomes compressed. The rapid rotation makes the gas settle into a rotating disk, and in some cases, newly born protostars shoot out jets in opposite directions along the axis of rotation. The only known explanation for these jets are magnetic field lines that bec0me twisted by the disk's rotation.
 Although a protostar might appear like a real star it still
lacks the ability to sustain itself. All the energy it has comes from
gravitational contraction, not from nuclear fusion. To ignite fusion it must
first contract further to rise the temperature within. A protostar
usually radiates away about half of its energy while the other half still
remains trapped at the core , raising the temperature. Thermal energy is then
transported from the center to the surface of the protostar by convection until
radiative diffusion-the traveling of photons from the core to the surface-
takes over. Eventually when the core exceeds 10 million K, hydrogen fusion can
occur, and the protostar becomes a true star! This star is said to be a
main sequence star burning hydrogen in it's core. Stars can range in
sizes depending on how much matter was gathered during the accreting
process. There are "failed stars" called brown dwarfs*, that do not
fuse hydrogen, but are thought to have been created in the same way stars do.
Although a protostar might appear like a real star it still
lacks the ability to sustain itself. All the energy it has comes from
gravitational contraction, not from nuclear fusion. To ignite fusion it must
first contract further to rise the temperature within. A protostar
usually radiates away about half of its energy while the other half still
remains trapped at the core , raising the temperature. Thermal energy is then
transported from the center to the surface of the protostar by convection until
radiative diffusion-the traveling of photons from the core to the surface-
takes over. Eventually when the core exceeds 10 million K, hydrogen fusion can
occur, and the protostar becomes a true star! This star is said to be a
main sequence star burning hydrogen in it's core. Stars can range in
sizes depending on how much matter was gathered during the accreting
process. There are "failed stars" called brown dwarfs*, that do not
fuse hydrogen, but are thought to have been created in the same way stars do.*Protostar: an early stage of the formation of a star when no nuclear fusion taking place at its core.
*nuclear fusion: When temperatures are high enough, nuclei, that would usually repel eachother, smash together due to their high speeds, and form heavier nuclei.
*Brown dwarfs: the reason it fails at becoming a true star is because its mass is so small that when gravity causes it to contract there comes a point when it becomes too packed together that eventually electron degeneracy pressure takes over before the core reaches a sufficiently high temperature to fuse hydrogen into helium. Electron degeneracy pressure just means that no to electrons can occupy the same quantum state.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)